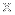This composite image of data from three different telescopes shows an ongoing collision between two galaxies, NGC 6872 and IC 4970 (roll your mouse over the image above). X-ray data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory is shown in purple, while Spitzer Space Telescope's infrared data is red and optical data from ESO's Very Large Telescope (VLT) is colored red, green and blue.
Astronomers think that supermassive black holes exist at the center of most galaxies. Not only do the galaxies and black holes seem to co-exist, they are apparently inextricably linked in their evolution. To better understand this symbiotic relationship, scientists have turned to rapidly growing black holes — so-called active galactic nucleus (AGN) — to study how they are affected by their galactic environments.
The latest data from Chandra and Spitzer show that IC 4970, the small galaxy at the top of the image, contains an AGN, but one that is heavily cocooned in gas and dust. This means in optical light telescopes, like the VLT, there is little to see. X-rays and infrared light, however, can penetrate this veil of material and reveal the light show that is generated as material heats up before falling onto the black hole (seen as a bright point-like source).
Despite this obscuring gas and dust around IC 4970, the Chandra data suggest that there is not enough hot gas in IC 4970 to fuel the growth of the AGN. Where, then, does the food supply for this black hole come from? The answer lies with its partner galaxy, NGC 6872. These two galaxies are in the process of undergoing a collision, and the gravitational attraction from IC 4970 has likely pulled over some of NGC 6872's deep reservoir of cold gas (seen prominently in the Spitzer data), providing a new fuel supply to power the giant black hole.
This image features two galaxies, NGC 6872 and IC 4970. The image is dominated by violet and red colors, while the shape of the image resembles a spiral galaxy being pulled or stretched out by two of its arms, with some very large bright sources very close by. NGC 6872 and IC 4970 are two galaxies in the process of colliding and merging. IC 4970 is a small galaxy at the top of the image that, thanks to Chandra X-ray Observatory (violet) and Spitzer infrared data (red), is shown to contain an active supermassive black hole. This composite image also includes optical data from the Very Large Telescope, which is mostly in yellow, white and green-grey. The gravitational attraction from IC 4970 has likely pulled over some of NGC 6872's deep reservoir of cold gas (seen prominently in the red Spitzer data), providing a new fuel supply to power the giant black hole.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||